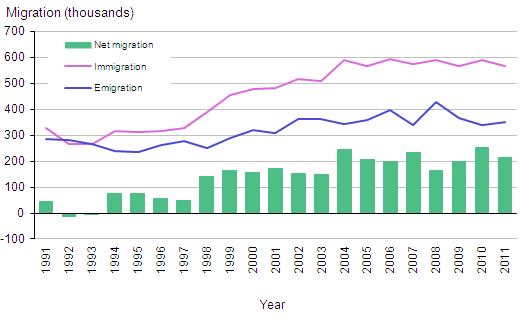
International migration estimates cover the flows and characteristics of long-term migrants between the UK and the rest of the world. These are people who intend to migrate for a period of at least one year. Statistics are available for short-term migrants (who migrate for less than one year).
Publications
Flag 4 records indicate international in-migrants who register with an NHS GP. This dataset indicates, for each local authority in England and Wales, the number of new Flag 4 records added to the Patient Register during the mid-year to mid-year period.

Quarterly and annual statistics relating to those: coming to the UK; extending their stay (temporarily or permanently); gaining citizenship; applying for asylum; and being detained or removed, as well as immigration for work, study and family reasons.

The MN Series present statistics on flows of international migrants to and from the UK and England and Wales.

Summary report of sources which can be used to estimate long-term international migration in Northern Ireland.

Annual report presenting and analysing UK migration data for the calendar year. This is a cross-government product.

Quarterly summary of migration trends, including links to new data from ONS, DWP, the Home Office and NRS. Data associated with this report include; provisional Long-Term International Migration (LTIM) and provisional International Passenger Survey (IPS) estimates of long term international migration, National Insurance number allocations to adult overseas nationals and control of immigration data. Other data released alongside the report include; population by country of birth and nationality and interregional migration.
This statistical bulletin details migration estimates that measure the movement of people in and out of Wales.

Statistics on non-UK nationals registering for a National Insurance number for the purposes of work, benefits or tax credits.

Estimates of short-term migration, based on information gathered by the International Passenger Survey (IPS) when migrants return home. Estimates refer to flows to and from England & Wales as well as the average stock of short-term migrants present in or absent from England & Wales. Statistics are provided for migration of periods between 3 and 12 months and 1 and 12 months.
Overview
Long-Term International Migration
The most comprehensive estimate of long-term migration into and out of the UK is Long-Term International Migration (LTIM). It is based primarily on migrants interviewed in the International Passenger Survey (IPS), but this survey does not include all types of migrants so the data are combined with other administrative sources.
LTIM is a combination of:
-
IPS flows
-
international migration to and from Northern Ireland
-
adjustments for people who change their intentions (switchers), and
-
adjustments for asylum seekers and their dependents
Some detailed analyses are only possible when based upon IPS data alone, therefore the published tables are grouped according to whether they are based on LTIM or IPS only. LTIM estimates are available for 1991 onwards, whereas IPS estimates are available from 1975 onwards.
Short-Term International Migration
Estimates of short-term international migration based on the IPS have been developed by the Office for National Statistics to supplement the existing estimates of Long-Term International Migration. Estimates are currently only available at national level for England and Wales and are published on a mid-year basis with the earliest figures being for the year to mid-2004.
Further work is being undertaken to improve the timeliness and geographical coverage of these estimates.
Technical Data
Long-Term International Migration
In line with the UN definition, an international long-term migrant is defined by the Office for National Statistics as someone who moves to a new country for at least a year.
International migration is a key component of population change and is used in the production of population estimates and projections.
Long-Term International Migration (LTIM) is the most comprehensive estimate of long-term migration into and out of the UK. It is based primarily on a subset of the International Passenger Survey (IPS), namely those international passengers sampled by the IPS who are migrants entering or leaving the UK by principal air, sea and tunnel routes. The IPS component is supplemented with:
-
data on international migration to and from Northern Ireland from the Northern Ireland Statistics and Research Agency (NISRA)
-
Home Office administrative data, which is used to calculate an adjustment for asylum seekers and their dependants not counted by the IPS, and
-
an adjustment for visitor switchers (those who intend to enter or leave Great Britain for less than 12 months but will actually stay, or stay away, for longer) and migrant switchers (those who intend to enter or leave Great Britain for at least 12 months without those intentions being realised)
Long-Term International Migration = IPS flows + Northern Irish flows + asylum seeker flows + visitor switcher flows - migrant switcher flows.
The estimates are published by citizenship; country of last or next residence; country of birth; main reason for migration; usual occupation; area of destination or origin within the UK; age and sex; sex and marital status; intended length of stay, actual length of stay; and route.
These flows do not indicate whether someone stays or leaves permanently. Therefore, they may not be added up on an annual basis to produce estimates of the population by country of birth or nationality.
The full methodology to estimate Long-Term International Migration can be viewed on the Office for National Statistics website.
Short-Term International Migration
Estimates of short-term international migration are based on a range of definitions developed in consultation with users:
-
UN definition of short-term international migration (visits for between 3 and 12 months for employment or study)
-
Separate employment and study estimates (lasting 3 to 12 months)
-
Estimates of visits for all reasons lasting 3 to 12 months
-
Each of the above but covering visits lasting between 1 and 12 months
Estimates are published as flows and also as stocks. The stock estimate refers to the average population present during the period and is supplemented by average length of stay. Both stock and flow estimates are published with associated standard errors.
Short-term international migration estimates are based on IPS data. However, unlike long-term international migration estimates, the IPS data used are based on interviews taking place at the end of each visit and so are not based on intentions. It is possible to use this different type of IPS data as, by definition, all short-term migration moves are completed 12 months after the move began, unlike long-term migrants who may never return to their country of origin.
Glossary
-
A10
The ten countries that joined the EU on 1 May 2004. These are Cyprus, the Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Poland, Slovakia and Slovenia.
-
A12
The 12 countries that joined the EU on 1 May 2004 and 1 January 2007. These are Cyprus, the Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Poland, Slovakia and Slovenia in 2004, Bulgaria and Romania in 2007.
-
A2
Refers to Bulgaria and Romania. These two countries joined the European Union on 1 January 2007. In previous published tables the A2 referred to Cyprus and Malta, but this has now been changed to conform with the other, more commonly used definition.
-
A8
The eight Central and Eastern European accession countries that joined the EU on 1 May 2004. These are the Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Slovakia and Slovenia.
-
APS
Annual Population Survey. This is the Labour Force Survey plus various sample boosts.
-
Calibration
An estimation procedure that constrains sample-based estimates of auxiliary variables to known totals (or accurate estimates). Calibration is used to improve the regional distribution of immigrants.
-
Citizenship
The nationality of the passport that the traveller is carrying.
-
Coefficient of variation
The coefficient of variation indicates the robustness of each estimate. This is sometimes shown as the standard error percentage on some tables. It is defined as (Standard error of the estimate divided by the Estimate) x 100.
-
Coherent reporting
Under this initiative, key information on migration and migration-related statistics collected across government are now jointly released. This allows for a principal point of access to these statistics and added value to the outputs in terms of insight, expert analysis and commentary to describe the similarities or differences between the data and why these occur.
-
Confidence interval
A range within which the true value of a population parameter lies with known probability. For example the 95 per cent confidence interval represents the range into which there are 19 chances out of 20 that the true figure would fall (had all migrants been surveyed). This is obtained as +/- 1.96 times the standard error.
-
Country of usual residence
The country in which a person has a place to live, where he or she normally spends the daily period of rest. Temporary travel abroad for purposes of recreation, holiday, visits to friends and relatives, business, medical treatment or religious pilgrimages does not change a person’s country of usual residence (UN-based definition).
-
E-Borders
A programme being led by the Home Office to create a joined-up modernised intelligence-led border control and security framework. It will capture information on all people entering and leaving the UK and is expected to provide a new source for producing international migration statistics for the UK. e-Borders is expected to become fully operational in 2014.
-
EEA
European Economic Area consists of the EU Member States plus Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway.
-
Emigrant (Outflow)
A person who leaves their country of usual residence to take up residence in another country for a period of at least 12 months.
-
Estimate
An indication of the value of an unknown quantity based on observed data.
-
EU15
European Union as constituted between 1 January 1995 and 1 May 2004. The following 15 member states were included: Austria, Belgium, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, the Irish Republic, Italy, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, Sweden and the UK. For the purpose of producing international migration estimates between the UK and the rest of the EU15, the UK is excluded from this grouping. However, by convention, this grouping is still referred to as the EU15.
-
EU25
European Union as constituted between 1 May 2004 and 1 January 2007. The following 25 member states are included: Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, the Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, the Irish Republic, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden and the UK. For the purpose of producing international migration statistics between the UK and the rest of the EU25, the UK is excluded from this grouping. However, by convention, this grouping is still referred to as the EU25.
-
EU27
European Union as constituted on 1 January 2007. The following twenty seven member states are included: Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Cyprus, the Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, the Irish Republic, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden and the United Kingdom. For the purpose of producing international migration statistics between the UK and the rest of the EU27, the UK is excluded from this grouping. However, by convention, this grouping is still referred to as the EU27.
-
EU accession countries
The 12 countries that have joined the EU15 since 1 May 2004. These are Bulgaria, Cyprus, the Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Poland, Romania, Slovakia and Slovenia.
-
GAD
Government Actuary’s Department which used to have responsibility for producing the national population projections. These responsibilities passed to the Office for National Statistics on 31 January 2006 who produced the 2006-based projections published in October 2007. GAD advises on a wide range of actuarial issues relating to social security, occupational pensions and pensions policy.
-
Immigrant (Inflow)
A person arriving or returning from abroad to take up residence in a country for a period of at least 12 months.
-
IMPS
Improving Migration and Population Statistics. The IMPS project aims to improve the accuracy of the Office for National Statistics population estimates and to establish where it is possible to introduce changes to data sources and methods that will improve the quality of the statistics. Further information on this project can be found on the National Statistics website.
-
In-country asylum seekers
Those asylum seekers who enter the UK and do not apply on arrival at port but apply for asylum while in the UK.
-
Interdepartmental Task Force on Migration
A cross-government initiative set up by the Office for National Statistics (ONS) in May 2006 to identify timely improvements that could be made to international migration statistics, in advance of those that might flow from long-term strategic initiatives such as e-Borders. The Task Force is being taken forward as part of the IMPS work already being carried out by ONS to improve migration and population statistics.
-
IPS
International Passenger Survey.
-
IPS counting line
A predetermined line that if crossed by passengers makes them eligible for sampling by the IPS.
-
LFS
Labour Force Survey - a quarterly household survey run by the Office for National Statistics.
-
Long-term international migrant
Someone who moves to a country other than that of his or her usual residence for a period of at least a year so that the country of destination effectively becomes his or her new country of usual residence. From the perspective of the country of departure the person will be a long-term emigrant and from that country of arrival the person will be a long-term immigrant (based on UN definition).
-
Long-Term International Migration (LTIM)
Long-Term International Migration is produced by combining migration data from the IPS, international migration to and from Northern Ireland, Home Office data on asylum seekers and adjustments for visitor switchers and migrant switchers.
-
Mid-year population estimate
The estimated resident population on 30 June of the reference year. Estimates are based on the previous mid-year estimate aged on and adjusted for births, deaths, migration and changes in mobile sub-groups in the year to 30 June.
-
Migrant switchers
Travellers who stated the intention in the IPS to stay in the destination country for more than a year, therefore, counted as migrants but who actually left sooner.
-
Migration filter shifts
Extra samples carried out on arrivals and departures to boost the sample of migrants. These are carried out at the four Heathrow and two Gatwick terminals.
-
Moving average
A way of smoothing a set of data to reduce short-term variability and make longer term trends more apparent.
-
National Population Projections
These are prepared by the Office for National Statistics who, in consultation with the devolved administrations, produce projections for the UK and its four constituent countries. A new set of projections is normally made every second year, based on a full-scale review of the trends affecting the underlying assumptions about fertility, mortality and migration.
-
Net emigration
More people are migrating out of a country (for at least 12 months) than are entering that country in a given time period.
-
Net immigration
More people are migrating into a country (for at least 12 months) than are leaving that country in a given time period.
-
Net migration
The numerical difference between immigration and emigration.
-
Non-contacts
A person counted by the IPS but not interviewed. For example, during peak periods an interviewer may not finish an interview before their next assigned contact has crossed the IPS counting line.
-
Non-response
Failure to obtain any survey information due to respondent refusal, non-contact or inability to reply.
-
Non-sampling error
Error attributable to all other sources other than sampling. Non-sampling errors may arise from many different sources. These may include misunderstanding or misreporting by respondents, variations between the way interviewers administer the survey, non-coverage of the population due to an inadequate sampling frame or sample design and errors made when processing the data.
-
NSQR
National Statistics Quality Review.
-
Port asylum seekers
Those asylum seekers who apply for asylum at UK ports.
-
Port health channel
A route sampled separately from other ordinary channels at one of the principal ports. People passing through a Port Health Channel include passengers referred from other desks including many who hope to stay in the UK for 6 months or longer and those referred for a medical examination.
-
Response rate
A measure of the proportion of people contacted who respond to the survey.
-
Safe third country
A safe country through which an asylum seeker passed en route to the UK.
-
Sampling error
The difference between an estimate derived from a random sample and the true population value; the difference being attributable to the fact that only a sample of values was used. That is, sampling error results because not every migrant who enters or leaves the UK is interviewed.
-
Sampling frame
A list of units used to select the sample.
-
Sampling interval
In systematic sampling, sampling is done by, for example, taking individuals at equally spaced intervals.
-
Standard error (SE)
An indication of the accuracy of an estimate and how much a sample estimate is likely to differ from the true value because of random effects.
-
Stratification (stratified)
Partitioning the population into subsets (strata) before the independent selection of a sample within each of these subsets.
-
Systematic sampling
Sampling where units are sampled at fixed intervals from a list or flow, beginning at a random start less than the fixed interval.
-
Visitor switchers
Visitors who enter or leave the UK intending to stay in the destination country for less than a year but who actually stay for a year or longer.
-
Weight
The number of migrants represented by each contact is given by the weight variable. The total number of migrants can therefore be calculated by summing the weights values of the contacts.
-
Workers Registration Scheme (WRS)
Worker Registration Scheme which is for A8 citizens who are in employed in the UK.
Contact Details
For statistical enquiries about this topic, please contact:
Migration Statistics Unit
Email: migstatsunit@ons.gsi.gov.uk
Telephone: +44 (0) 13 2944 4097
Office for National Statistics Segensworth Road Fareham PO15 5RR