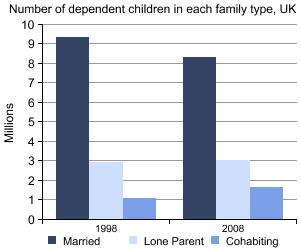
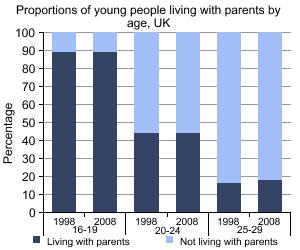
This topic explores the population size and social characteristics of families, children and young people. Family statistics cover married or cohabiting couples, lone parents, civil partners and same-sex couples. This includes families with no children, dependent children or non-dependent children.
Publications

Presents statistics on adoptions in England and Wales.

Presents figures about children looked after by local authorities in Wales.

Finalised data for all births, deaths, marriages, civil partnerships and divorces along with population data for the year in question.
Carers' Statistics for Northern Ireland presents quarterly figures at a regional and Health and Social Care Trust level for completed and declined carers' assessments, re-assessments and reviews.

The Census paints a big picture of society and is a benchmark at the start of the 21st Century. Census 2001 commentaries look in a little more depth at the 'big picture' for the UK, and provide commentary on aspects of a topic in England and Wales as a whole, and on topics in Wales or the English regions. The counts that the commentaries are based on come from the Key Statistics for local authorities in England and Wales released in February 2003.
Annual update of the number of child healthy weight interventions undertaken by NHS boards. This data is used to monitor HEAT Targets.

This bulletin presents first release summary statistics on children's social care in Northern Ireland for year ending 31 March. Where data are available, each section will provide information on the latest annual figures including a Trust breakdown, detailed commentary, and an overview of how the latest annual figures compare to recent trends. The bulletin is based on Children Order Returns used to collect aggregated statistics on children in need, child protection and looked after children.

The cohabitation estimates add to the legal marital status population estimates by reflecting the numbers co-residentially in each marital status category.
Presents recent estimates of the number of families by type, people in families by family type and children in families by type. Types of family include married couple families, cohabiting couple families and lone parent families. Tables on household size, household types and people in different household types are also provided. These include estimates of people living alone, multi-family households and households where members are all unrelated.

Information collected from the Family Resources Survey.

This report analyses families in the UK by the number of dependent children they have, with focus on those with three or more dependent children, examining trends over time, where such families live and their economic activity.
A statistical digest that looks at family types and explores similarities and differences between them. It also examines the relationship between families and health, unpaid care and education.

Statistics on fostering and adoption intermediary services.
This report presents a range of statistical targets and indicators in support of the Northern Ireland Executive’s anti poverty and social inclusion strategy ‘Lifetime Opportunities'. The monitoring framework is structured around 3 ‘layers’: • Child poverty targets • Poverty and social inclusion indicators • Public service agreement targets Analyses of statistics are on a lifecycle basis and are benchmarked against other jurisdictions when possible
This is an evaluation based on the Integrated Household Survey (IHS) experimental data, collected between April 2009 - March 2010.

A report on research using the National Statistics Omnibus Survey produced on behalf of the Ministry of Justice and the Department for Children, Schools and Families.

Looks at data from the Family Resources Survey classified by urban/rural regions.
This report analyses the characteristics of young adults aged between 20 and 34 who live with their parents.
Overview
Families in the UK
Most of us live in families and most of us live in households containing one family. Many of these are ‘traditional’ families of a married couple with children, but increasingly people are experiencing family life within a cohabiting couple or a lone parent family. The recent patterns of family dynamics – the decline and delay of marriage and child-bearing, and the increase in divorce, cohabitation and births outside marriage – also mean that individuals are more likely to experience a greater variety of family structures throughout their lifetimes. Consequently there is an increasing minority who live in ‘reconstituted’ families as family units break up and reform.
Children and Young People
An understanding of families is crucial for those involved in planning and decision-making at the national and local level. Moreover, at one time or another, every member of society is part of, or affected by, his or her family situation. This is particularly true for children and young people, and it is therefore important to examine the lives of children and young people in contemporary UK society. This includes information on their characteristics, experiences, wellbeing and lifestyle, in addition to population estimates of children and young people and the family types in which they live.
Technical Data
The Census and most government surveys, including the General Household Survey (GHS) and the Labour Force Survey (LFS), collect statistical data on households and their members. As a result, there are a number of different sources available, each with their own purpose and advantages.
Data from the LFS provides a large sample of all people in households. It gives UK-wide coverage of all major family types. The LFS has provided full and comprehensive family data since 1996 when the relationship matrix was introduced.
The GHS is a survey of households in Great Britain, which has been carried out since 1971. It provides households and families data over a longer period of time than the LFS, but is based on a smaller sample of the population of Great Britain. The family information section of the GHS allows more detail, such as analysis of relationship histories.
The Census can be used for more detailed analysis. For example, analysis by lower level geography (county, borough or ward level), age and ethnic group. More detailed breakdowns of family types in the UK, such as by the age and number of children, are also possible.
Other sources of data, such as registered life events and other social surveys, are used to illustrate the trends and patterns that influence family and household formation. Life events include information on marriages, divorces, civil partnerships and adoptions.
Glossary
-
Children
Unless otherwise specified, children are usually defined as those aged 16 and under. However, in some cases other age breakdowns are used, and it is common in family statistics to extend the definition of children to include all dependent children. See: Dependent children
-
Cohabiting or cohabitation
In the 2001 Census, living arrangements are calculated by combining the responses to the questions on legal marital status and the relationship question. In the General Household Survey (GHS) and Labour Force Survey (LFS), living arrangements are asked directly in the questionnaires. One of the main reasons for analysing living arrangements is so that cohabiting couples can be identified. Cohabiting couples may be married or have any other marital status.
-
Dependent child
Defined in the census, the Labour Force Survey (LFS) and the General Household Survey (GHS), as a child living with their parent or parents, who is under 16-years-old or aged 16 to 18 in full-time education. It does not include any children who have a spouse, partner or child living in the household.
-
Family
A married or cohabiting couple with or without children or a lone parent. Children may be dependent or non-dependent. In the General Household Survey (GHS) and Census, cohabiting couple families include same-sex couples. A family can also consist of a grandparent or grandparents with a grandchild or grandchildren if the parents of the child or children do not usually live in the household. In the 2001 Census, less than one per cent of all families were a grandparent family.
-
Household
A person living alone or a group of people who have the same address as their only or main residence and with common housekeeping. For example, the 2001 Census defined this as those who either share one meal a day or share the living accommodation. Although definitions differ slightly across surveys and the census, they are very similar. Households do not include people living in communal establishments.
-
Living arrangements
See Cohabitation.
-
Lone parent family
Defined in the 2001 Census as a father or mother living with his or her child or children. This is providing that the children do not have a spouse, partner or child in the household. A lone parent family can also be a grandparent with a grandchild or grandchildren. This is providing that the child or children have no parents living in the household. The LFS definition is a lone parent living with his or her never-married children. This is providing that these children have no children of their own living with them. The GHS definition is one parent, regardless of sex, living with his or her never-married dependent children. This is providing these children have no children of their own.
-
Marital status
The legal marital status of an individual or couple. The introduction of Civil Partnerships in 2005 expanded the possible responses to questions on legal marital status. The 2007 Labour Force Survey (LFS) available responses are: single (never married); married (living with husband or wife); married (separated from husband or wife); divorced; widowed; a civil partner in a legally-recognised civil partnership; in a legally-recognised civil partnership and separated from his or her civil partner; formerly a civil partner, the civil partnership now legally dissolved; or a surviving civil partner: his or her partner having since died.
-
Non-dependent children
Children aged 16 and over living with their parent or parents who have no spouse, partner or child living in the household. The definition does not include those aged 16 to 18 in full-time education.
-
Relationship matrix or relationship grid
A major change to information collected about households and families in the 1993 GHS was the introduction of the relationship matrix question. The new question asked about the relationship of every household member to every other household member. Before this question was introduced, the survey used to only ask the relationship of every household member to the head of the household. The relationship matrix question is now used in the LFS and was used in the 2001 census. As well as identifying family units, the matrix helps statisticians to group individuals in different ways. For example, extended families and other relationships are recognised.
-
Young people
Young people are usually defined as those aged over 16 and under 25, however in some cases other age breakdowns are used.
Contact Details
For statistical enquiries about this topic, please contact:
ONS Customer Contact Centre
Email: info@statistics.gsi.gov.uk
Telephone: +44 (0)845 601 3034 Minicom/textphone: 01633 812399
Office for National Statistics Post: Room 1015 Government Buildings Cardiff Road Newport NP10 8XG