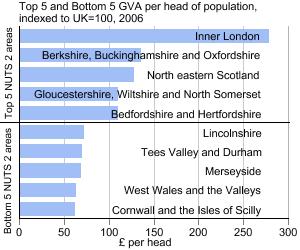
Regional accounts are a regional specification of the equivalent accounts of the whole UK economy. In the regional accounts, each region is treated as a separate economic entity and the accounts cover Gross Value Added (GVA) and Gross Disposable Household Income (GDHI).
Publications

These reports have been produced for each English region to coincide with the official launch of the new ONS Regional Statisticians teams, established in each English Government Office Region in April 2007. Each report provides a profile of the relevant region and presents a range of statistics that help to understand differences between regions. Within regions, comparisons are made between sub-regions and between rural and urban areas. Regional statistics in the context of the European Structural Funds are discussed, followed by a look-ahead at the developments in regional statistics expected as a result of the Allsopp programme, three years since the original Allsopp Report.

Two papers that aim to complement Impact Evaluation Framework+ (and other guidance) by examining the sources, existing methods and concepts which surround the measurement of the impact of Interventions or Investments consistent with methods used to produce official Gross Value Added (GVA) estimates.
Estimates of sub-regional (NUTS2) Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF) at current purchasers' prices by NUTS 1 and NUTS 2 areas, 1998 to 2000. Estimates were not produced for subsequent years.

Shows economic activity as measured by Gross Value Added (GVA) for English regions, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland including component totals and industry group totals.
Regional (NUTS1) Gross Value Added estimates at constant prices using a production approach.

Annual regional household income news release, article and tables from Regional Accounts for English regions, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.
Results of a pilot exercise to compile quarterly output indices for the nine English regions. This release aims to provide a further proof of concept and allow regional users a view of the effects of the current economic recession.

Provides access to a wide range of information in different areas of the UK

Regional Trends is a comprehensive regular source of official statistics for the Statistical Regions of the UK (Scotland, Wales, Northern Ireland and the Government Office Regions within England). It includes a wide range of demographic, social, industrial and economic statistics, covering aspects of life in the regions.

Regional Trends Online Tables is a comprehensive regular source of official statistics for the Statistical Regions of the UK (Scotland, Wales, Northern Ireland and the Government Office Regions within England). It includes a wide range of demographic, social, industrial, and economic statistics, covering aspects of life in the regions.
Sub-regional estimates of Government Output, Government Gross Adjusted Disposable Income and Government Capital Expenditure.
Overview
The economic territory of the country as a whole is broken down into three levels, using the Nomenclature Units of Territorial Statistics (NUTS) classification. The top level is NUTS1, comprising the Wales, Scotland, Northern Ireland and the nine Government Office Regions (GORs) of England. The 37 NUTS2 sub-regions divide the UK into counties, groups of counties or groups of local authorities. The 133 NUTS3 areas mainly comprise counties and unitary authorities.
In addition, there is an extra-region territory identified. This comprises the economic activity that cannot be assigned to a particular region, such as overseas embassies and armed forces bases and offshore oil and gas extraction.
All data published by regional accounts are annual, at current basic prices (that is, the effects of inflation are not removed and taxes on products are excluded, while subsidies on products are included). They are consistent with the European System of Accounts 1995 (ESA95) which provides the legal framework for the production of the estimates. GVA at NUTS2 level is used in the allocation of structural funds from the EU to deprived regions.
Regional GVA is published in December each year, with a breakdown by industry – 31 industries at NUTS1, 17 at NUTS2 and 6 at NUTS3. Regional GDHI is published in the spring following the GVA publication, with detailed component breakdowns at NUTS1 and 2 and just the balances published at NUTS3.
Technical Data
The regional accounts methodology guide is available at: National Statistics Online - Product - Regional Gross Value Added (GVA).
Regional Gross Value Added (GVA)
GVA is the value added by any unit engaged in production. Regional GVA is measured at current basic prices, which is: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) less taxes on products plus subsidies on products.
The NUTS1 series in its current format starts in 1989. NUTS2 and NUTS3 series start in 1995.
The production of regional GVA is a legal requirement under ESA 95 and informs regional funding decisions taken by the EU. The requirements are to produce regional GVA annually, at current prices and broken down into six industries.
GVA can be estimated using either the production or the income approaches. The UK uses the income approach and is developing a production approach.
The production approach involves measuring the value of goods and services produced and removing the value of goods and services used up in the production process. The income approach involves adding up all the income earned by resident units in the production of goods and services.
The main components of income-based GVA are: compensation of employees, gross operating surplus, mixed income (income from self-employment) and taxes (less subsidies) on production.
A ‘top down’ approach is used to calculate regional figures, whereby the national aggregate is allocated to regions using the most appropriate regional indicator available.
The National Accounts totals (consistent with the latest UK National Accounts Blue Book publication) used to constrain the regional GVA estimates are broken down by component of income and industry. Regional GVA for the latest year is estimated and published on a provisional basis and will be subject to significant revisions following the compilation of the relevant supply and use tables.
Regional Gross Disposable Household Income (GDHI)
Gross disposable household income (GDHI) is the amount of money that the household sector has available for spending or saving. This is money left after expenditure associated with income, for example, taxes and social contributions, property ownership and provision for future pension income.
The production of regional GDHI is a legal requirement of the European Commission and the methods and data used are consistent with the guidance set out in ESA 95. Current price GDHI estimates and components are supplied to Eurostat at the NUTS2 level. These data may support arguments in the debate about the relative welfare of regions across the UK and the EU area.
Regional GDHI estimates are published annually for the period 1995 to t-2 years (t being the year of publication), consistent with the latest Blue Book.
Numerous data sources are used in the production of regional GDHI to estimate the distribution of income across the UK. These comprise both survey and administrative data that conform as far as possible to international guidance.
Resources of the household sector are classified as either primary or secondary. Primary incomes are received as the result of individuals’ participation in the production process, such as employees providing labour or through the ownership of assets and/or from self-employment. Secondary incomes are received as the result of redistribution of income, for example, pensions and benefits.
Uses of the household sector are also classified as either primary or secondary. Primary uses consist of rent on land and interest paid on mortgages and other borrowing. Secondary uses are mainly non-discretionary payments, like taxes and social contributions to National Insurance.
Household disposable income is defined as the sum of resources less uses and represents the amount available to the household sector for spending on consumption or saving.
A ‘top-down’ approach is used for the production of regional GDHI estimates, whereby the national aggregate is allocated to regions using a regional indicator.
Glossary
-
Annual Business Inquiry (ABI)
A business survey carried out by the Office for National Statistics (ONS). Part 1 collects employment data, while part 2 collects financial information including GVA, net capital expenditure and compensation of employees. A regional apportionment model is used to obtain NUTS1, 2 and 3 level data.
-
Annual Survey of Hours and Earnings (ASHE)
An Office for National Statistics survey that provides regional information about the levels, distribution and make-up of earnings and hours worked for employees in all industries and occupations.
-
Basic prices
Basic prices are the preferred method of valuing output and value added. They reflect the amount received by the producer for a unit of goods or services excluding any taxes on products and including any subsidies on products. This price includes only taxes on production (for example, business rates) and excludes any subsidies on production (for example, agricultural set-aside).
-
Blue Book
The Blue Book is the Office for National Statistics' key annual publication for national statistics and provides detailed estimates of national product, income and expenditure for the UK. It covers value added by industry, full accounts by sector - including financial and non-financial corporations, central and local government and households - and capital formation.
-
Capital consumption
The estimated amount of capital resources used up in the process of production in any period.
-
Current price
Current price figures measure value of transactions in the prices relating to the period being measured.
-
Depreciation
See capital consumption.
-
European system of accounts (ESA)
The European framework providing the conceptual and legal background for national accounts.
-
Expenditure and Food Survey (EFS)
The EFS is an Office for National Statistics (ONS) survey of household expenditure, food consumption and income.
-
Extra-Regio
This accounts for economic activity that cannot be assigned to any specific region. For the UK, this consists of offshore oil and gas extraction and the activities of UK embassies and forces overseas.
-
Gross disposable household income (GDHI)
The money that the household sector has left for spending and saving after deducting non-disccretionary payments such as taxes, pension contributions and interest from its total income.
-
Gross domestic product (GDP)
A measure of the value of goods and services produced in the UK before providing for capital consumption. It is equal to gross value added (GVA) at basic prices plus taxes less subsidies on products. Alternatively, it is equal to the sum of total final domestic consumption expenditures plus exports less imports of goods and services.
-
Gross trading profits/surplus
Profits of privately owned corporations and surpluses of local authorities, central government bodies and public corporations, gross of deductions for capital consumption.
-
Gross value added (GVA)
This is a measure of the contribution to Gross Domestic Product (GDP) made by an individual producer, industry or sector. The GVA generated by any unit engaged in production activity can be calculated as the residual of the units’ total output less intermediate consumption, or as the sum of the factor incomes generated by the production process. Net value added is shown after deducting capital consumption.
-
Headline series
Series which have been smoothed using a five-point moving average to reduce volatility.
-
Labour Force Survey (LFS)
A quarterly Office for National Statistics (ONS) survey of UK households that collects information on respondents’ personal circumstances and labour market availability.
-
Mixed income (MI)
Income from self-employment.
-
Nomenclature of units for territorial statistics (NUTS)
This was created by the European Office for Statistics (Eurostat) as a single hierarchical classification of spatial units used for statistical production across the EU. At the top of the hierarchy are the individual Member States of the EU, below that are levels 1 to 3 (see appendix A).
-
Non-profit institutions serving households (NPISH)
Non-profit institutions serving households include organisations such as charities, universities, churches, trade unions and members’ clubs. NPISH institutions receive their principal resources from voluntary contributions from households as well as payments made by the government.
-
Output
This is the value of goods and services together with work-in-progress produced. It is equal to the value of sales plus any increase, less any decrease, in the value of inventories of finished products and work in progress. Output is therefore measured after deducting holding gains. The outputs of the distribution and service trades industries are calculated net of the value of goods bought for resale without further processing.
-
Pay as you earn (PAYE)
Income tax withheld from employees’ wages and paid directly to the government by the employer.
-
Public corporations
These are public trading bodies that have a substantial degree of financial independence from the public authority, central or local government that created them.
-
Raw series
Unsmoothed series (see Headline series).
-
Regional indicator
A measure of economic activity by region.
-
Rental income
Income from the ownership of buildings.
-
Residence basis
Where gross value added (GVA) is allocated to where the income is received.
-
Short-term Turnover and Employment Survey (STES)
An Office for National Statistics (ONS) business survey that collects data on turnover and employees.
-
Smoothed series
See Headline series.
-
Sole trader
A business owned and controlled by one person.
-
Standard Industrial Classification (SIC)
This is the industrial classification applied to the collection and publication of a wide range of economic and industrial statistics. The current version is SIC (2003), based on NACE Rev 1 which is the statistical classification of economic activities for the EU.
-
Standard statistical region (SSR)
SSRs are similar but do not equate to NUTS1 regions. The latter are used for the production of Regional Accounts in the UK.
-
Subsidies on production
These are subsidies based on the levels of productive activity, for example, numbers employed.
-
Subsidies on products
These are subsidies based on a quantity or value of goods or services sold.
-
Supply and use table
Supply and use tables show the total availability (supply) of individual products (goods and services) by industry, for use in the economy from both domestic production and imports.
-
Survey of Personal Incomes (SPI)
Supply and use tables show the total availability (supply) of individual products (goods and services) by industry, for use in the economy from both domestic production and imports.
-
Tangible asset
An asset such as a building or piece of equipment that has physical properties.
-
Taxes on production
These are taxes paid by producers, for example, business rates, motor vehicle duties and regulatory fees, which are levied according to production, and do not depend on the profitability or otherwise of a company.
-
Taxes on products
These taxes are defined as product-specific taxes, for example, value added tax (VAT), excise duties, air passenger tax, insurance premium tax and import duties and are based on the volume or value of production sold.
-
Top down approach
The national totals are allocated to the regions by means of regional indicators.
-
Workplace basis
The gross value added (GVA) is allocated to where the income is generated, that is where the production activity takes place.
Contact Details
For statistical enquiries about this topic, please contact:
Pete Lee
Email: pete.lee@ons.gsi.gov.uk
Telephone: +44 (0) 207 014 2093
Zone GR41 Office for National Statistics I Myddelton Street London EC1R 1UW