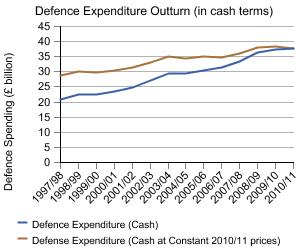
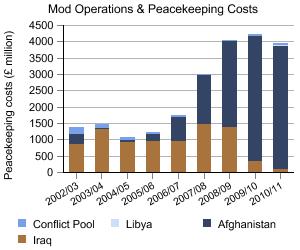
This topic provides details on the composition and scope of Ministry of Defence (MOD) expenditure including where and on what the budget is spent. It also provides information on the impact of defence spending on the wider economy, detailed estimates of the defence inflation and international comparisons.
Publications

The statistical notice will present a chain-linked Laspeyres price index and corresponding year-on-year price growths for personnel expenditure, contract expenditure and overall defence inflation

The annual statistics compendium of the Ministry of Defence

A summary of the annual statistics compendium of the Ministry of Defence

A summary of the annual statistics compendium of the Ministry of Defence

War Pensions statistics.
Overview
Published statistics on finance in the UK Defence Statistics 2011 cover the following areas:
Departmental resources
Statistics include:
-
changes in defence expenditure
-
breakdown of defence expenditure outturn
-
estimates of MOD equipment procurement expenditure
-
net book values for MOD Fixed Assets
-
MOD’s estimated expenditure on Research & Development
-
external income earned by MOD
Defence Inflation
Information on defence inflation including:
-
estimates of defence inflation from 2005/06 to 2010/11 as a whole and by contract type and labour costs
-
a comparison of general inflation in the UK economy with defence inflation
Industry
Information on the MOD’s spending on equipment and services in the UK, including:
-
the estimated amount of money MOD spent with UK industry broken down by industrial grouping
-
recent MOD payments on PFI projects and planned spend for next year
-
statistics on procurement spend with MOD’s top 10 suppliers
Trade
Information on defence trade, including:
-
estimates of total export orders for defence equipment and services
-
the estimated value of MOD Balance of Payments for Trade in Services
Contracts
Information on contracts placed, major equipment projects and payments, including:
-
the number and value of contracts placed
-
a list of defence suppliers paid £5m or more
-
a list of private sector holding companies paid £50m or more
International defence
Information on MOD’s commitment internationally including comparisons with NATO and the rest of the world, including:
-
estimated costs incurred by MOD in respect of operations and peacekeeping
-
defence expenditure expressed as % of a nations GDP for each of the NATO countries
-
top 15 military spenders worldwide
-
selected comparisons of UK defence expenditure and manpower to other NATO allies
Technical Data
Departmental resources
The majority of the data in UK Defence Statistics (UKDS) tables 1.1, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5, 1.6, 1.8) are obtained directly from Ministry of Defence (MOD) Defence Resources and are consistent with figures published in the MOD Annual Report and Accounts.
Public Expenditure by Departmental Grouping (UKDS Table 1.2) is taken from Public Expenditure Statistical Analyses (PESA 2011). It examines the expenditure on defence within the wider public expenditure framework.
Research and development
Research and development (R&D) expenditure (UKDS table 1.7) is broken down into R&D activity undertaken inside and outside the MOD. Data are derived from an annual survey of MOD R&D expenditure and from MOD accounting systems. R&D activity is classified within the Organisation for Economic Co-operation & Development’s Frascati Guidelines which align to National Accounts definitions. Revisions and changes to these statistics are described in Defence Statistics bulletin 6 and Defence Statistics bulletin 1 and 2.
Defence Inflation
Data used to compile Table 1.9a, 1.9b, 1.9c and 1.9d comes from a number of different sources and more information on the methodology used and the source of the data can be found in Defence Statistics Bulletin 10.
Industry
Estimated Defence Expenditure Outturn in the UK, by Industry Group (UKDS table 1.10) is prepared from MOD administrative systems. Figures exclude ‘internal’ expenditure such as pay and allowances. Industrial groups are derived from the Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) guidelines maintained by ONS. From 1996/97 to 2007/08 figures are based on SIC 1992, prior to this they are based on SIC (80). For 2008/09 onwards, industrial groupings are based on the 2007 Standard Industrial Classification.
Charts and tables 1.12 a-d describe MOD procurement expenditure with its top 10 suppliers. These statistics are compiled from data obtained from DBS Finance.
Trade
Estimates of Identified Export Orders (UKDS table 1.13) is prepared from data provided by the UK Trade and Industry Defence and Security Organisation, which they collect from an annual survey of known defence contractors.
Balance of Payments (UKDS table 1.14) is a measure of the UK’s trading account with the rest of the world. Trade in Services are provisions of services between UK residents and non-residents, and transactions in goods which are not freighted out of the country in which they take place; these transactions are not recorded in the official ‘Trade in Goods’ statistics. More details can be found in Defence Statistics Bulletin 4.
Statistics on the number and value of new contracts let by the MOD (UKDS Table 1.15) are compiled based upon information submitted by MOD commercial officers to DBS Finance.
Contracts
Information on Equipment Projects comes from the Major Projects Report and shows details of projects at both the pre- and post Main-Gate stage of their development.
A list of organisations paid £5 million or more by MOD (UKDS table 1.17) is compiled from data obtained from DBS Finance.
International defence
Information used in Table 1.18 comes from the MOD Annual Report and Accounts. Information contained in Tables 1.19, 1.20 and 1.21 comes from data gathered by NATO and the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI). Charts 1.22 a-d are constructed from publicly available sources, see UK Defence Statistics 2011 for more information.
Background Quality Reports are available for all these statistics are available on the DASA website. They provide further information about the data sources and methodology used to construct these tables
Glossary
-
Annual business inquiry (ABI)
The ABI is a business survey that gathers data from businesses to produce estimates of employee jobs by industry and geography. It also offers a breakdown of businesses by type.
-
Assets
Assets can be financial or non-financial. Financial assets include monetary gold, bank deposits, IMF Special Drawing Rights, Loans granted bonds, shares, accounts receivable, and the value of the government’s stake in public corporations. Non-financial assets consist of fixed capital (such as buildings and vehicles); stock, land and valuables.
-
AUC
Assets Under Construction.
-
Balance sheet
The balance sheet is a financial statement showing the assets, liabilities, and net worth of a business on a specified date.
-
Capital consumption
Capital consumption is also called depreciation and represents the amount of fixed capital used up each year.
-
Chain-linked index
An index which relates the value of the current period to a previous period, not a fixed base period. Chain-linking indices allows the basket of goods to be regularly updated without introducing a break in the series.
-
Clear Line of Sight (CLoS)
The method for reporting and controlling defence spending changed in 2010/11 (for Budgets) and will change in 2011/12 (for Estimates & Accounts (Outturns)) following Treasury plans to simplify the control framework. The Clear Line of Sight (CLoS) Alignment project aims to ensure consistency in presentation as well as promoting better value for money). See Resource Accounting & Budgeting Section in Chapter 1 for more further information.
-
Constant prices
At ‘constant prices’ indicates a quantity from which the effects of inflation have been removed. The constant prices will refer to a year as the basis for the calculation, for example ’constant 2001/02 prices’.
-
Current expenditure
Current expenditure on goods and services is the sum of expenditure on pay, and related staff costs, plus spending on good and services. It is net of receipts from sales. It excludes capital expenditure, but includes expenditure on equipment that can only be used for military purposes since that is counted as current expenditure. It differs from final consumption in that capital consumption is not included.
-
Current prices
See Outturn prices.
-
DBS Finance
DBS Finance provides expert information, advice and services to and on behalf of MOD business areas. They are responsible for payments to MOD suppliers totalling more than £27 billion a year, and for recovering £2 billion of receipts in respect of MOD invoices. See also DBA and FMSSC.
-
Defence analytical services and advice
DASA was created in July 1992 and provides National Statistics on Defence and other corporate information, forecasting and planning and consultancy, advice and research services to the Ministry of Defence. It ceased to be an agency on 1 April 2008 and was renamed Defence Analytical Services and Advice.
-
Defence bills agency
The DBA is primarily responsible for paying bills submitted to the Ministry of Defence by defence contractors. The DBA formally ceased to be a Defence Agency as at 1 April 2007 and forms part of the Financial Management Shared Service Centre.
-
Defence budget
Under Cash Accounting, the amount of money planned to be spent during a financial year is the defence budget. Under RAB, the sum of resources planned to be consumed during a financial year is the defence budget. This excludes the additional expenditure on current operations that are funded from year to year by HM Treasury. See Resource budgeting.
-
Defence Inflation
Defence inflation is the average rate of increase in pay and prices of all goods and services making up the Defence budget after allowing for changes in quality and quantity.
-
Defence Support Group
As of 1 April 2008, the Army Base Repair Organisation (ABRO) and the Defence Aviation Repair Agency (DARA) merged to form the Defence Support Group. DSG is a Trading Fund established to support the Armed Forces and deliver wider defence objectives in support of the key Defence Industrial Strategy requirements.
-
Departmental Annually Managed Expenditure
Departmental Annually Managed Expenditure is spending that is outside the DEL, but included in departmental budgets. This includes the provision for Armed Forces Pensions and non-cash items such as depreciation, cost of capital charges, and provision. Previously these non-cash items were not subject to the same controls and were included in AME, but from 2003/04 they were included as part of the DEL.
-
Departmental Expenditure Limit (DEL)
The DEL is a firm plan for three years for a specific part of a department’s expenditure. In general the DEL will cover all running costs and all programme expenditure except, in certain cases, where spending is included in departmental AME because it cannot reasonably be subject to close control over a three-year period. DELs are divided into current resource and capital budgets.
-
Departmental Resource Accounts (DRAc)
The Ministry of Defence is required to prepare resource accounts for each financial year detailing the resources acquired, held, or disposed of during the year, and the way it has used them during the year.
-
Depreciation
Depreciation is also termed capital consumption. Total Managed Expenditure (TME) includes public sector expenditure gross of the depreciation of capital assets used to produce non-market services. Public sector net investment deducts an aggregate charge for all depreciation (market and non-market) from gross capital spending.
-
Enabling Contract
Enabling contracts provide an efficient and effective means of procuring goods and services where requirements arise on a regular basis, combining the benefits of reduced process costs and enhanced buying power resulting from a consolidation of requirements.
-
Estimated prices
They are forecasts of the prices expected to pertain when the expenditure occurs. These are presented to Parliament.
-
Financial Management Shared Service Centre
The FMSSC was established in April 2007, bringing together several existing Ministry of Defence (MOD) back-office finance processes including the former Defence Bills Agency (DBA). Based at sites in Liverpool and Bath, the FMSSC is customer focused and has responsibility for overseeing end-to-end accounting processes. Its mission is to deliver high quality financial management services to support the MOD’s decision making, internal and statutory reporting activities. FMSSC was incorporated into the DBS in July 2011.
-
Frascati manual
The Frascati Manual is an internationally recognised methodology for collecting and using R&D statistics. It includes definitions of basic concepts, guidelines for collecting data and the classifications to be used in compiling statistics, which in turn allow for international comparisons to be made. See also SSAP 13.
-
Gross domestic product (GDP)
GDP (at market prices) is the value of goods and services produced within a country’s borders in a year. Economic data are often quoted as a percentage of GDP to give an indication of trends through time and to make international comparisons easier.
-
Gross Domestic Product Deflator
The GDP deflator is an implicit price deflator for the Gross Domestic Product and is derived by dividing the estimate of GDP at current prices by the estimate of GDP at constant prices. The GDP Deflator can be viewed, and is commonly used, as a measure of inflation in the economy for the country to which it refers.
-
Gross national product (GNP)
GNP is the total value of goods and services produced in a year by a country’s nationals, including profits from capital held abroad.
-
Holding company
Refers to companies that are full or part owners of other companies (subsidiaries and joint ventures).
-
Intangible assets
Most if not all of the Ministry of Defence’s intangible assets are development costs. Under Statement of Standard Accounting Practice 13 (SSAP 13), pure research costs, and applied research costs that are not immediately linkable to a product cannot be put in the Balance Sheet as assets. Only development costs which lead to the introduction into service of new products or systems can be put on the Balance Sheet.
-
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
IFRS are principles-based Standards, Interpretations and the Framework adopted by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). See Resource Accounting & Budgeting Section in Chapter 1 for more information.
-
Laspeyres price Index
Laspeyres price Index is a measure of the change in the price of a basket of goods. The quantity of the items within the basket of goods are fixed to allow a measure of pure price change. Prices are aggregated in a Laspeyeres index by using weights from the base period and prices in the base year are normalised to equal 100.
-
Major Projects Report (MPR)
The MPR is the Department’s annual report to Parliament on progress in equipment procurement. It provides a summary of each project’s current status and progress to date. It also provides comparisons on current forecast costs and in-service dates.
-
Market exchange rate
The Market Exchange Rate is a currency exchange rate determined largely by market forces.
-
Miscellaneous Contracts
The payment method employed by DBS Finance (the MOD’s primary bill paying authority) for running service items such as the provision of utilities. Such items are covered by “miscellaneous” transactions where no 'MOD HQ Contract' exists. These agreements for goods or services will have been set up locally between the MOD Branch and the Supplier and are legally binding.
-
National Audit Office
The NAO scrutinises public spending on behalf of Parliament. It is totally independent of government. It audits the accounts of all government departments and agencies as well as a wide range of other public bodies, and report to Parliament on the economy, efficiency and effectiveness with which government bodies have used public money.
-
NATO
North Atlantic Treaty Organisation.
-
Near Cash
Near Cash describes departmental resource budgets less non-cash charges. The main non-cash charges currently included in budgets are depreciation and impairments, cost of capital, stock write-off, national audit fees, bad debts, profit and loss on disposal of fixed assets and movement in provisions. The term near cash is used rather than cash because it remains on an accruals basis and does not reflect the timing of actual cash payments.
-
Net-cash requirement
The NCR is the amount of actual money that Ministry of Defence requires from the Government in order to fund its activities. The NCR takes account of the movements in working capital levels (debtors, creditors and stocks) but not non-cash costs.
-
Non-cash items
Non-cash items in Annually Managed Expenditure (AME) include various notional transactions such as depreciation and cost of capital that appear in the operating cost statement under RAB and which are recorded in AME for the period of Spending Review 2000, rather than in DEL.
-
Novated Contract
A novated contract is a contract which has been taken on by a new Contractor/Supplier following an agreement with the original owner of the contract.
-
Operating cost statement
The Operating Cost Statement is the statement in departmental resource accounts that shows the current income and expenditure on an accrual basis. It is similar to the profit and loss statement on commercial accounts. Now called the Statement of Comprehensive Net Expenditure (SOCNE).
-
Outturn and estimated outturn
Outturn describes expenditure actually incurred, whereas estimated outturn describes estimated expenditure on the basis of actual expenditure to date.
-
Outturn prices
Outturn prices are the prices of the period when the expenditure actually occurred; also described as current prices.
-
Parliamentary Annual Estimates
The Main Parliamentary Estimates start the supply procedure and are presented to Parliament around the start of the financial year to which they relate. Main Estimates are contained in the annual Departmental Reports and can be found on departmental websites.
-
Pink book
Detailed annual estimates of the UK balance of payments including estimates for the current account (trade in goods and services, income and current transfers), the capital account, the financial account and the International Investment position.
-
Private Finance Initiatives
The PFI is a system for providing capital assets for the provision of public services. Typically, the private sector designs, builds and maintains infrastructure and other capital assets and then operates those assets to sell services to the public sector. In most cases, the capital assets are accounted for on the balance sheet of the private sector operator.
-
Public Expenditure Statistical Analyses
PESA is a compendium that gathers recent outturn data, estimated outturns for the latest year, and spending plans over the entire range of UK public expenditure.
-
Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
PPP is a method of measuring the relative purchasing power of different countries’ currencies over the same types of goods and services. Because goods and services may cost more in one country than in another, PPP allows us to make more accurate comparisons of standards of living across countries. PPP estimates use price comparisons of comparable items but since not all items can be matched exactly across countries and time, the estimates are not always ‘robust.’
-
R&D
Research and Development
-
Real Defence Spending
Real Defence Spending figures are adjusted for the effect of general price inflation relative to a base year, as measured by the GDP market price deflator.
-
Resource accounting
Resource accounting is the accounting system that will henceforth be used to record expenditure in the departmental accounts instead of cash accounting. It applies generally accepted accounting practice (GAAP) used in private industry and other government departments to departmental transactions. Spending is measured on an accruals basis.
-
Resource budget
The resource budget is the sum of a department’s resource Departmental Expenditure Limit and resource Annually Managed Expenditure. It is the budget for current expenditure on an accruals basis.
-
Resource budgeting
Resource budgeting is the budgeting regime adopted for the spending plans set in the 2000 Spending Review. It is derived from resource accounting rules, but there are several differences in treatment between resource accounts and resource budgets.
-
Retail Price Index
The RPIX excludes mortgage interest payments. It is a chain-linked price index measuring the change in prices of a basket of goods and services purchased by a typical household. RPIX is a commonly used measure of inflation in the general economy.
-
RfR
Request for Resources: RfR1 = Provision of Defence Capability, RfR2 = Net additional cost of operations, RfR3 = War Pensions and Allowances.
-
Single Use Military Equipment
Single use military equipment are Ministry of Defence held assets that are only suitable for military purposes (such as warships), as apposed to dual-use equipment which can also be used for non-military purposes.
-
SSAP 13
Statement of Standard Accounting Practices No.13 gives guidance on the accounting policies to be followed in respect of research and development expenditure. The guidance aligns to the OECD Frascati definitions for measuring Research & Experimental Development. See also Frascati Manual.
-
Standard Industrial Classification (SIC)
SIC classifies business establishments and other statistical units by the type of economic activity in which they are engaged. The classification is maintained by the Office for National Statistics (ONS).
-
Statement of Parliamentary Supply
The Statement of parliamentary supply is the Parliamentary accountability statement. It reports to Parliament on resource outturn, a comparison of outurn against the Supply Estimate and a summary of income not Appropriated in Aid and payable to the Consolidated Fund.
-
Terms of Business Agreement
Terms of Business Agreement aims to create a more disciplined interface between the key acquisition parties (e.g. MOD and DSTL). It will strengthen the relationship between the main parties involved in acquisition.
-
Total managed expenditure
TME is a definition of aggregate public spending derived from national accounts. It is the consolidated sum of current and capital expenditure of central and local government, and public corporations. TME is the sum of the Departmental Expenditure Limit and Annually Managed Expenditure.
-
Urgent Operational Requirements (UoR)
UORs are equipment items that are required urgently for a specific military operation. Where the requirement is new or unforeseen, and specific to a particular operational theatre, it will funded from the Government Reserve rather than the Defence budget.
Contact Details
For statistical enquiries about this topic, please contact:
Defence Analytical Services and Advice
Email: dasa-enquiries-mailbox@mod.uk
Telephone: Tel: +44 (0) 20 7807 8792
Defence Analytical Services and Advice 3-K-15 MOD Main Building Whitehall London SW1A 2HB