Latest statistics on causes of death in the United Kingdom and constituent countries, including alcohol-related deaths, suicides, drug-related deaths, deaths involving MRSA and Clostridium difficile, and estimates of excess winter mortality.
Publications

Number of Alcohol Related Deaths Registered in Northern Ireland

Alcohol-related deaths in the United Kingdom, England and Wales, and government office regions in England.

Finalised data for all births, deaths, marriages, civil partnerships and divorces along with population data for the year in question.

Presents data on infant deaths that have been linked to their corresponding birth record. These birth cohort tables relate to deaths among infants born in a given calendar year.
The number of child deaths which have been reviewed by Child Death Overview Panels (CDOPs) in the year ending 31 March, including the number which were assessed as having modifiable factors.

Presents statistics on stillbirths, infant deaths and childhood deaths occurring annually in England and Wales. Also contains data on cause of death, sex and age-group plus analyses by some of the key risk factors affecting stillbirths and infant deaths including age of mother and birthweight.

Present data on death registrations in England and Wales. They contain data for death rates, cause of death data by sex and age and death registrations by area of residence.

Number of deaths registered in Northern Ireland where Clostridium Difficile was mentioned on the death certificate.

Number of deaths registered in Northern Ireland where MRSA was mentioned on the death certificate.

This release presents figures for deaths where Clostridium difficile (C. difficile) was mentioned on the death certificate: by sex, age group and place of death, in England and Wales. National data are available for 1999 and for 2001 onwards.

This release presents figures for deaths where meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) was mentioned on the death certificate: by sex, age group and place of death, in England and Wales. National data are available from 1993 onwards.

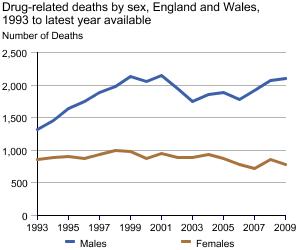
Contains data on deaths related to drug poisoning in England and Wales from 1993 onwards, by cause of death, sex, age and substances involved in the death.

Number of drug related deaths and deaths due to drug misuse registered in Northern Ireland.

The number of, and trends in, drug-related deaths in Scotland, broken down by, for example, age, sex, Health Board and Council areas and whether particular types of drug were found in the body.

A measure of the increase in winter mortality, provided on an annual basis, in the form of the excess winter mortality figure.

This volume builds on the tradition of undertaking in-depth analyses of mortality by area in decennial supplements to annual statistical publications. It covers the 1990s and, for the first time, takes a broader view of health outcomes than are reflected by mortality alone. It includes reviews of variations in congenital anomalies, cancer incidence, adult and infant mortality, births, conceptions and abortions. Data are presented for the UK and constituent countries, regions, and local areas.

Live births and infant deaths by gestational age. Additionally by birthweight, multiplicity of births, mother's age, marital status (registration type), father's occupation and ethnic group.

These tables include data on live births, infant deaths, and infant mortality rates by ethnic group as well as on infant deaths, and infant mortality rates by cause of death and ethnic group.

Presents annual data on deaths from injury and poisoning in England and Wales using a matrix of mechanism by intent developed by the International Collaborative Effort (ICE) on injury statistics.
This reports examines trends in the stillbirth rate by known risk factors to explore the increase in the stillbirth rate in 2002 in England and Wales.
Leading causes of death by age group and sex
The indicator measures the change in Life expectancy at birth in Working Neighbourhood Fund (WNF) areas which are also Spearhead areas.
Health profiles for all LA areas presenting a range of indicators and a snapshot of the overall health of the local population.

Mortality monitoring

This publication has been discontinued following a consultation on restructuring ONS mortality statistics. The last volume published was Mortality statistics: Cause, 2005 (Series DH2 No. 32). Presents statistics on deaths occurring annually in England and Wales.

Presents mortality statistics on deaths registered in England and Wales, classified by sex and age and by other selected information collected at the time of registration.

Present data on death registrations in England and Wales. They contain data for death rates, cause of death data by sex and age and death registrations by area of residence.

Mortality monitoring.
Scotland's National Drug Related Deaths Database which will include wide ranging information about people who have died from a drug-related death, including contact history and substitute prescribing information.

A joint ONS/Health & Safety Executive report on the analysis of death registrations to ascertain statistical associations between specific occupations and various causes of death.
The number of child deaths which have been reviewed by Child Death Overview Panels (CDOPs), including the number which were assessed as preventable.
Compendium of public health outcomes indicators presented at England and upper tier LA level. Indicators are split over 4 domains: improving the wider determinants of health; health improvement; health protection; healthcare, public health and preventing premature mortality.

Births registered in England and Wales are linked to birth notifications records to utilise key variables. These linked records are further linked to death registration records. This permits publication of live births and infant deaths by ethnicity and gestational age, and additionally by birthweight, multiplicity of births, mother's age, marital status (registration type) and father's occupation. This release reports on the data subnationally.
Gives results of the ICD-10 v2010 bridge coding study which shows the impact of the new ICD-10 software update on stillbirths and neonatal deaths by cause of death.
Gives results of the ICD-10 v2010 bridge coding study, which shows the impact of the new ICD-10 software update on mortality statistics by cause of death.
Scotland data added to the WHO database of 600 health/health-related indicators for over 50 countries in Europe (including UK), for 1970 to the present, where available. Data are presented in a user-friendly, graphical or tabular form, allowing time trend and international comparisons. Accompanying briefing notes provide a summary of the findings and some interpretation.

This report reviews perinatal mortality over a variety of time periods (from 33 years to 15 years), depending on the dataset and describes some of the changes since data collection started. The data is collected across Scotland and therefore represents changes in the whole population.
Report from the Scottish Suicide Information Database (ScotSID) and covers suicides occurring in each calendar year. The aim of the database is to provide a central repository for information on all probable suicide deaths in Scotland in order to support epidemiology, preventive activity and policy making. The report provides information covering demographic information, contact with health services and related health data.
Annual update of suicide deaths information (numbers and rates by sex), analysed at Scotland, NHS board and LA level and by deprivation decile at Scotland level.

Suicides in the United Kingdom, England and Wales, and government office regions in England.

The 20th Century mortality files are a record of mortality in England & Wales from 1901 to 2000. The files consist of an aggregated database of deaths by agegroup, sex, year and underlying cause, and include populations for England & Wales.

The 21st Century Mortality Files are a record of mortality in England and Wales from 2001 onwards. They are designed to complement the 20th Century Mortality Files, which are a record of mortality in England and Wales from 1901 to 2000. The files consist of an aggregated database of deaths by age-group, sex, year and underlying cause, and include populations for England and Wales.

Report reviewing perinatal mortality over a variety of time periods

Report on unexplained infant deaths in England and Wales which includes both sudden infant deaths and deaths for which the cause remained unknown or unascertained.

These tables provide annual and quarterly data for a selection of key statistics under the following themes: population, demography and health. Figures for the latest quarters and years may be provisional, these will be updated to final figures when data is available.
Overview
The Office for National Statistics (ONS) reports annually on specific causes of death: alcohol-related deaths and suicides in the UK, and drug-related deaths, deaths involving MRSA and Clostridium difficile, and estimates of excess winter mortality in England and Wales.
The General Register Office for Scotland and the Northern Ireland Statistics and Research Agency also report on similar causes of death for their respective countries.
The Department of Health (DH) publishes an annual Mortality Monitoring Bulletin (based on ONS data) which monitors trends in all-age-all-cause mortality, and deaths from cancer, circulatory diseases, suicide and injury of undetermined intent, and accidents, for England and the former Spearhead Group (areas which had the worst health and deprivation).
Technical Data
Deaths in the UK are coded using the International Classification of Diseases (ICD). At present, the Tenth Revision (ICD-10) is used by each constituent country. Mortality data for England and Wales are held by the Office for National Statistics (ONS), and data for Scotland and Northern Ireland are held by the General Register Office for Scotland (GROS) and the Northern Ireland Statistics and Research Agency (NISRA) respectively.
The Centre for Health Analysis and Life Events (CHALE) at ONS produces summary tables of death registrations in England and Wales and annual reports for the following causes of death:
Alcohol-related deaths in the United Kingdom
The National Statistics definition of alcohol-related deaths only include those causes regarded as being most directly due to alcohol consumption. It does not include other diseases where alcohol has been shown to have some causal relationship. The definition includes all deaths from chronic liver disease and cirrhosis (excluding biliary cirrhosis). Apart from deaths due to poisoning with alcohol (accidental, intentional or undetermined), this definition excludes any other external causes of death, such as road traffic and other accidents.
Numbers and rates of alcohol-related deaths for the UK, England and Wales, and government office regions in England, for 1991 onwards are available.
Suicides in the United Kingdom
Suicide is defined as deaths given an underlying cause of intentional self-harm or injury/poisoning of undetermined intent. In England and Wales, it has been customary to assume that most injuries and poisonings of undetermined intent are cases where the harm was self-inflicted but there was insufficient evidence to prove that the deceased deliberately intended to kill themselves. This cannot be assumed in children due to the possibility that these deaths were caused by unverifiable accidents, neglect or abuse. Therefore, only adults aged 15 years and over are included in the figures.
Numbers and rates of adult suicides (ages 15 and over) for the UK, England and Wales, and government office regions in England, for 1991 onwards are available.
The National Statistics definition of drug-related deaths includes mental and behavioual disorders due to drug use (excluding alcohol and tobacco), accidental, intentional or undetermined poisoning by drugs, medicaments and biological substances, and assault by drugs, medicaments and biological substances. Figures are available for specific substances. There is also a drug misuse indicator which is defined as deaths where the underlying cause was drug poisoning, abuse or dependence and where any of the substances controlled under the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 were involved. Further information is available at the link above.
Numbers and rates of deaths related to drug poisoning and drug misuse for England and Wales, for 1993 onwards are available.
Deaths involving MRSA and Clostridium difficile
Meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus MRSA) is a variety of Staphylococcus aureus that is resistant to meticillin, and some of the other antibiotics that are usually used to treat Staphylococcus aureus. Staphylococcus aureus is a common germ that lives completely harmlessly on the skin and in the nose of about one third of the population. It can cause problems if it has the opportunity to enter the body, which is more likely to happen in people who are already unwell.
Clostridium difficile (C. difficile) occurs when normal, healthy intestinal bacteria are subdued by the use of antibiotics. This allows C. difficile to flourish in the gut and produce a toxin that causes diarrhoea. People over the age of 65 are more susceptible to contracting infection.
The number of deaths due to MRSA and C. difficile is difficult to estimate. Trends in mortality are normally monitored using the underlying cause of death (the disease or injury which initiated the train of events leading directly to death). However, MRSA and C. difficile are often not the underlying cause of death. Those who die with MRSA or C. difficile infections are usually patients who were already very ill, and it is their existing illness, rather than the infection, which is often designated as the underlying cause of death. Figures for deaths where MRSA and C. difficile were the underlying cause of death and also where they were mentioned as contributory factors are therefore produced.
Numbers and rates of deaths involving MRSA and Clostridium difficile for England and Wales, for 1993 onwards and 1999 onwards respectively are available.
Excess winter mortality is calculated as winter deaths (deaths occurring between December and March) minus the average of non-winter deaths (deaths occurring in the preceding August to November and the following April to July). This produces a number of excess winter deaths that is rounded to the nearest 10 for final data and to the nearest 100 for provisional data.
Figures for all ages and broad age groups (0-64, 65-74, 75-84, 85+) for England and Wales and government office regions in England, for 1991/92 onwards are available.
For more detailed information about the methods and quality of each output, please see the specific links above.
Additional reports and peer-reviewed articles on causes of death are often published as part of the Health Statistics Quarterly journal.
ONS has published the 20th century mortality and 21st century mortality files, which contain records of mortality split by sex, age group and underlying cause of death, for England and Wales, for 1901 to 2000 and 2001 to the latest year available respectively. Population data and ICD dictionaries are also included in the files.
The Department of Health (DH) publishes an annual Mortality Monitoring Bulletin (based on ONS data) which monitors trends in all-age-all-cause mortality, and deaths from cancer, circulatory diseases, suicide and injury of undetermined intent, and accidents, for England and the former Spearhead Group (areas which had the worst health and deprivation).
Glossary
-
Accelerated registrations
The process by which a death can be registered at the time of adjournment of an inquest, instead of having to await the outcome of criminal proceedings.
-
Alcohol-related deaths
Cause of death is defined in the alcohol-related deaths report and downloadable data set using the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision (ICD-9) for the years 1991 to 2000, and the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) for 2001 onwards.
-
Alcohol-related deaths, ICD-10 codes
Alcohol-related deaths are defined using the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) codes: F10 (mental and behavioural disorders due to use of alcohol), G31.2 (degeneration of nervous system due to alcohol), G62.1 (alcoholic polyneuropathy), I42.6 (alcoholic cardiomyopathy), K29.2 (alcoholic gastritis), K70 (alcoholic liver disease), K73 (chronic hepatitis, not elsewhere classified), K74 excluding K74.3-K74.5 (fibrosis and cirrhosis of liver, excluding biliary cirrhosis), K86.0 (alcohol induced chronic pancreatitis), X45 (accidental poisoning by and exposure to alcohol), X65 (intentional self-poisoning by and exposure to alcohol), and Y15 (poisoning by and exposure to alcohol, undetermined intent).
-
Alcohol-related deaths, ICD-9 codes
Alcohol-related deaths are defined using the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision (ICD-9) codes: 291 (alcoholic psychoses), 303 (alcohol dependence syndrome), 305.0 (non-dependent abuse of alcohol), 425.5 (alcoholic cardiomyopathy), 571.0 (alcoholic fatty liver), 571.1 (acute alcoholic hepatitis), 571.2 (alcoholic cirrhosis of liver), 571.3 (alcoholic liver damage, unspecified), 571.4 (chronic hepatitis), 571.5 (cirrhosis of liver without mention of alcohol), 571.8 (other chronic non-alcoholic liver disease), 571.9 (unspecified chronic liver disease without mention of alcohol) and E860 (accidental poisoning by alcohol).
-
Annual extract
The dataset taken from the main deaths database from which most mortality tabulations are derived.
-
Assault
The ICD-10 terminology referring to homicide and injuries inflicted by another person with intent to injure or kill, by any means (excluding deaths from legal intervention and operations of war).
-
Bridge coding
An exercise in which the same group of deaths are independently classified according to two different classifications or coding methods.
-
CHALE
Centre for Health Analysis & Life Events at the Office for National Statistics (ONS).
-
Clostridium difficile
C. difficile is a spore forming bacterium found naturally in the gut of a small proportion of the healthy adult population. C. difficile associated disease occurs when normal, healthy intestinal bacteria are subdued by the use of antibiotics. This allows C. difficile to flourish in the gut and produce a toxin that causes diarrhoea.
-
Comparability ratio
A measure, expressed as a ratio, indicating the net effect of the change in classification (from ICD-9 to ICD-10) on a particular cause of death.
-
Coroner
Public official responsible for the investigation of violent, sudden or suspicious deaths.
-
Deaths related to drug poisoning
Cause of death is defined in the ‘deaths relating to drug poisoning report’ and downloadable dataset using the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision (ICD-9) for the years 1993 to 2000, and Tenth Revision (ICD-10) for 2001 onwards. Deaths are included where the underlying cause was due to drug poisoning and where a drug controlled under the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 was mentioned on the death certificate.
-
Deaths related to drug poisoning, ICD-10 codes
Deaths relating to drug poisoning are defined using the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) codes: F11-F16, F18-F19 (mental and behavioural disorders due to drug use, excluding alcohol and tobacco), X40-X44 (accidental poisoning by drugs, medicaments and biological substances), X60-X64 (intentional self-poisoning by drugs, medicaments and biological substances), X85 (assault by drugs, medicaments and biological substances) and Y10-Y14 (poisoning by drugs, medicaments and biological substances, undetermined intent).
-
Deaths related to drug poisoning, ICD-9 codes
Deaths relating to drug poisoning are defined using the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision (ICD-9) codes: 292, 304, 305.2-305.9 (mental and behavioural disorders due to drug use, excluding alcohol and tobacco), E850-E858 (accidental poisoning by drugs, medicaments and biological substances), E950.0-E950.5 (intentional self-poisoning by drugs, medicaments and biological substances), E962.0 (assault by drugs, medicaments and biological substances) and E980.0-E980.5 (poisoning by drugs, medicaments and biological substances, undetermined intent).
-
Dual coding
The coding of the same data twice, using different methods of coding in order to assess inconsistencies.
-
Early neonatal deaths
Deaths at ages up to six completed days of life.
-
Epidemiologist
A person concerned with the incidence and distribution of diseases and other factors, including the environment, relating to health.
-
Excess Winter Mortality (EWM)
Estimates of excess winter deaths are based on the difference between the number of deaths during the four winter months (December to March) and the average number of deaths during the preceding four months (August to November) and the following four months (April to July).
-
External cause
Death resulting from accident or violence. An alternative term for the underlying cause of death. ICD codes from Chapter XX (see Secondary causes).
-
HSQ
Health Statistics Quarterly journal (an Office for National Statistics (ONS) quarterly publication).
-
Inquest
Inquiry into the cause of an unexplained, sudden or violent death held by a coroner.
-
International Classification of Diseases (ICD)
The ICD is the international standard diagnostic classification for all general epidemiological, many health management purposes and clinical use. It is used to classify diseases and other health problems recorded on many types of health and vital records including death certificates and health records. In addition to enabling the storage and retrieval of diagnostic information for clinical, epidemiological and quality purposes, these records also provide the basis for the compilation of national mortality and morbidity statistics.
-
MCCD
Medical Certificate of Cause of Death.
-
Modification rules
Rules used in ICD-10 applied rules to select the correct underlying cause of death.
-
Mortality rate
The usual practice in Office for National Statistics (ONS) publications is to calculate age-standardised mortality rates per 100,000 population, standardised to the European Standard Population. Age-standardised rates are used to allow comparison between populations which may contain different proportions of people of different ages.
-
MRSA
MRSA is a variety of Staphylococcus aureus that is resistant to meticillin, and some of the other antibiotics that are usually used to treat Staphylococcus aureus. Those who die with MRSA are usually patients who were already very ill and it is instead their existing illness, rather than MRSA, which is often designated as the underlying cause of death. There is therefore, an interest in the number of deaths where MRSA contributed to the death.
-
Neonatal
Relating to infants aged under 28 days.
-
NHSCR
National Health Service Central Register.
-
Perinatal deaths
Stillbirths and deaths at ages up to six completed days of life (early neonatal).
-
Population Trends
An Office for National Statistics (ONS) quarterly publication.
-
Postneonatal deaths
Deaths of infants aged 28 days and over but under one year.
-
Probability of survival
The Office for National Statistics (ONS) definition of the probability of survival to age 75 estimates the likelihood of a person surviving between birth and age 75. The probabilities of survival figures are based on the assumption that individuals would experience that year's age-specific mortality rates throughout their lives.
-
Registrar
Statutory officer responsible for the registration of births, deaths and marriages.
-
Registrar General
Statutory appointment with responsibility for the administration of the registration Acts in England and Wales, and other related functions as specified by the relevant legislation.
-
Registration officer
Generic term for registrar, superintendent registrar and additional registrars.
-
Reports
Short articles on cause of death using registration data soon after they are available (in the Health Statistics Quarterly and Population Trends journals).
-
RON
Registration online. A web-based system which enables registrars to record births, stillbirths, deaths and civil partnerships online.
-
RSS
Registration Service Software.
-
Rule 3
One of the rules used to select the correct underlying cause of death; its different use in ICD-10 results in significant differences from ICD-9 for some causes (see Selection rules).
-
Secondary cause
The nature of injury, or main injury, that caused death (where the underlying cause is assigned to an external cause from Chapter XX in ICD-10, V01 to Y89). Nature of injury codes are taken mostly from Chapter XIX (prefixes S and T).
-
Selection rules
Rules used in the ICD to determine the correct selection of the underlying cause of death (see Rule 3).
-
Sequela (sequelae)
A condition (or conditions) reported as the result of a previous injury, a ‘late effect’ (under ICD-9), or that occurs as a late effect one year or more after the originating event.
-
Spearhead group
The Spearhead Group consists of the 70 local authority areas that are in the bottom fifth nationally for three or more of the following five factors: male life expectancy at birth, female life expectancy at birth, cancer mortality rate in under 75s, cardiovascular disease mortality rate in under 75s, and Index of Multiple Deprivation 2004 (local authority summary), average score. For life expectancy, the ‘bottom’ fifth means those with the lowest figures; for mortality rates and deprivation scores, it means those with the highest figures.
-
Standardised mortality ratio (SMR)
An SMR is the ratio of the observed number of deaths in an area (for example, an electoral ward) to the number expected if that area had the same age-specific rates as a reference area (for example, England and Wales). If an SMR is less than 100, the number of deaths in an area was less than would have been expected. Conversely, if an SMR is greater than 100, the number of deaths was greater than expected.
-
Standard population
Used in the calculation of the age-standardised death rates; an element of the population (such as age and sex) is ‘held constant’ to control its effect, for example, the European Standard.
-
Stillbirth
Refers to the Stillbirth (Definition) Act 1992; a child born after 24 or more weeks completed gestation who did not show any signs of life at any time after being born.
-
Suicide & undetermined injury
Suicide is defined using the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision (ICD-9) codes E950-E959 and E980-E989, excluding E988.8 for the years 1991 to 2000, and the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) codes X60-X84 and Y10-Y34, excluding Y33.9 (where the coroner’s verdict was pending) for the years 2001 to 2006. ‘Coroner’s verdict pending’ deaths do not need to be excluded from deaths assigned to ICD-10 Y33.9 from 2007 onwards, since these deaths are now coded to ICD-10 U50.9.
-
Superintendent registrar
Statutory officer with responsibilities relating to births, deaths, marriage and other registration functions, as specified in the relevant legislation.
-
Underlying cause of death
The cause of death selected for primary tabulation based on ICD rules.
-
VSOB
Vital Statistics Outputs Branch (at the Office for National Statistics (ONS)).
-
WHO
World Health Organisation.
Contact Details
For statistical enquiries about this topic, please contact:
Claudia Wells
Email: mortality@ons.gsi.gov.uk
Telephone: +44 (0) 16 3345 5867
Centre for Health Analysis & Life Events (CHALE) The Office for National Statistics Government Buildings Cardiff Road Newport NP10 8XG